

计算机科学与探索 ›› 2022, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (12): 2860-2869.DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2103051
收稿日期:2021-03-16
修回日期:2021-05-08
出版日期:2022-12-01
发布日期:2021-04-29
通讯作者:
+E-mail: wangyan@lut.cn作者简介:王燕(1971—),女,甘肃泾川人,硕士,教授,CCF会员,主要研究方向为模式识别、人工智能。基金资助:Received:2021-03-16
Revised:2021-05-08
Online:2022-12-01
Published:2021-04-29
About author:WANG Yan, born in 1971, M.S., professor, member of CCF. Her research interests include pattern recognition and artificial intelligence.Supported by:摘要:
针对卷积神经网络在高光谱图像特征提取和分类的过程中,存在空谱特征提取不充分以及网络层数太多引起的参数量大、计算复杂的问题,提出快速三维卷积神经网络(3D-CNN)结合深度可分离卷积(DSC)的轻量型卷积模型。该方法首先利用增量主成分分析(IPCA)对输入的数据进行降维预处理;其次将输入模型的像素分割成小的重叠的三维小卷积块,在分割的小块上基于中心像素形成地面标签,利用三维核函数进行卷积处理,形成连续的三维特征图,保留空谱特征。用3D-CNN同时提取空谱特征,然后在三维卷积中加入深度可分离卷积对空间特征再次提取,丰富空谱特征的同时减少参数量,从而减少计算时间,分类精度也有所提高。所提模型在Indian Pines、Salinas Scene和University of Pavia公开数据集上验证,并且同其他经典的分类方法进行比较。实验结果表明,该方法不仅能大幅度节省可学习的参数,降低模型复杂度,而且表现出较好的分类性能,其中总体精度(OA)、平均分类精度(AA)和Kappa系数均可达99%以上。
中图分类号:
王燕, 梁琦. 快速3D-CNN结合深度可分离卷积对高光谱图像分类[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(12): 2860-2869.
WANG Yan, LIANG Qi. Fast 3D-CNN Combined with Depth Separable Convolution for Hyperspectral Image Classification[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2022, 16(12): 2860-2869.
| Layer(type) | Output shape | Parameter# |
|---|---|---|
| input_1(Input Layer) | (11,11,20,1) | 0 |
| Conv3d_1(Conv3D) | (9,9,14,8) | 512 |
| Conv3d_2(Conv3D) | (7,7,10,16) | 5 776 |
| Conv3d_3(Conv3D) | (5,5,8,32) | 13 856 |
| Reshape_1(Reshape) | (5,5,256) | 0 |
| Separable_conv2d_1(separable) | (3,3,64) | 18 752 |
| Separable_conv2d_1(separable) | (3,3,128) | 8 384 |
| Flatten_1(Flatten) | (128) | 0 |
| Dense_1(Dense) | (256) | 295 168 |
| Dropout_1(Dropout) | (256) | 0 |
| Dense_2(Dense) | (128) | 32 896 |
| Dropout_1(Dropout) | (128) | 0 |
| In total, 377 408 trainable parameters are required Train on 4 304 samples, validate on 1 845 samples | ||
表1 模型在Window Size大小为11×11的IP数据集上的参数
Table 1 Parameters of model on IP dataset with Window Size of 11×11
| Layer(type) | Output shape | Parameter# |
|---|---|---|
| input_1(Input Layer) | (11,11,20,1) | 0 |
| Conv3d_1(Conv3D) | (9,9,14,8) | 512 |
| Conv3d_2(Conv3D) | (7,7,10,16) | 5 776 |
| Conv3d_3(Conv3D) | (5,5,8,32) | 13 856 |
| Reshape_1(Reshape) | (5,5,256) | 0 |
| Separable_conv2d_1(separable) | (3,3,64) | 18 752 |
| Separable_conv2d_1(separable) | (3,3,128) | 8 384 |
| Flatten_1(Flatten) | (128) | 0 |
| Dense_1(Dense) | (256) | 295 168 |
| Dropout_1(Dropout) | (256) | 0 |
| Dense_2(Dense) | (128) | 32 896 |
| Dropout_1(Dropout) | (128) | 0 |
| In total, 377 408 trainable parameters are required Train on 4 304 samples, validate on 1 845 samples | ||
| 指标 | NumComponents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| Kappa×100 | 99.11 | 99.61 | 98.77 | 99.47 |
| OA/% | 99.21 | 99.65 | 98.92 | 99.53 |
| AA/% | 97.84 | 99.78 | 98.91 | 99.67 |
表2 基于IP数据集的不同降维大小下的分类精度
Table 2 Classification accuracy of different dimension reduction sizes based on IP dataset
| 指标 | NumComponents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| Kappa×100 | 99.11 | 99.61 | 98.77 | 99.47 |
| OA/% | 99.21 | 99.65 | 98.92 | 99.53 |
| AA/% | 97.84 | 99.78 | 98.91 | 99.67 |
| Window size | IP | PU | SA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa×100 | OA/% | AA/% | Tr_time/s | Kappa×100 | OA/% | AA/% | Tr_time/s | Kappa×100 | OA/% | AA/% | Tr_time/s | |
| 9×9 | 99.08 | 99.19 | 98.90 | 18.65 | 99.90 | 99.92 | 99.89 | 67.73 | 99.89 | 99.90 | 99.92 | 199.06 |
| 11×11 | 99.30 | 99.39 | 99.60 | 45.58 | 99.96 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 91.42 | 99.95 | 99.96 | 99.94 | 231.19 |
| 13×13 | 99.78 | 99.74 | 99.78 | 36.65 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 146.50 | 99.98 | 99.98 | 99.99 | 305.56 |
| 17×17 | 99.66 | 99.70 | 99.84 | 62.16 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 326.47 | 99.98 | 99.99 | 99.99 | 408.13 |
| 23×23 | 99.74 | 99.78 | 99.76 | 147.68 | 98.24 | 98.67 | 98.11 | 538.34 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 1 026.73 |
| 25×25 | 99.66 | 99.70 | 99.86 | 172.65 | 99.96 | 99.97 | 99.88 | 954.98 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 99.99 | 1 471.46 |
表3 3个数据集上空间维度大小对模型性能的影响
Table 3 Impact of spatial window size on proposed model on 3 datasets
| Window size | IP | PU | SA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa×100 | OA/% | AA/% | Tr_time/s | Kappa×100 | OA/% | AA/% | Tr_time/s | Kappa×100 | OA/% | AA/% | Tr_time/s | |
| 9×9 | 99.08 | 99.19 | 98.90 | 18.65 | 99.90 | 99.92 | 99.89 | 67.73 | 99.89 | 99.90 | 99.92 | 199.06 |
| 11×11 | 99.30 | 99.39 | 99.60 | 45.58 | 99.96 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 91.42 | 99.95 | 99.96 | 99.94 | 231.19 |
| 13×13 | 99.78 | 99.74 | 99.78 | 36.65 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 146.50 | 99.98 | 99.98 | 99.99 | 305.56 |
| 17×17 | 99.66 | 99.70 | 99.84 | 62.16 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 326.47 | 99.98 | 99.99 | 99.99 | 408.13 |
| 23×23 | 99.74 | 99.78 | 99.76 | 147.68 | 98.24 | 98.67 | 98.11 | 538.34 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 1 026.73 |
| 25×25 | 99.66 | 99.70 | 99.86 | 172.65 | 99.96 | 99.97 | 99.88 | 954.98 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 99.99 | 1 471.46 |
| Dataset | Index | 2D-CNN | 3D-CNN | Multi-scale-3D-CNN | Hybrid SN | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Pines | OA/% | 80.27 | 82.62 | 81.39 | 97.75 | 99.61 |
| AA/% | 68.32 | 76.51 | 75.22 | 97.54 | 99.65 | |
| Kappa×100 | 75.26 | 79.25 | 81.20 | 97.44 | 99.78 | |
| Salinas scene | OA/% | 96.34 | 85.00 | 94.20 | 98.06 | 99.96 |
| AA/% | 94.36 | 89.63 | 96.66 | 98.80 | 99.94 | |
| Kappa×100 | 95.93 | 83.20 | 93.61 | 97.85 | 99.95 | |
| Pavia University | OA/% | 96.63 | 96.34 | 95.95 | 98.40 | 99.97 |
| AA/% | 94.84 | 97.03 | 97.52 | 97.89 | 99.97 | |
| Kappa×100 | 95.53 | 94.90 | 93.40 | 97.89 | 99.96 |
表4 不同方法下的实验性能对比
Table 4 Comparison of experimental performance under different methods
| Dataset | Index | 2D-CNN | 3D-CNN | Multi-scale-3D-CNN | Hybrid SN | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Pines | OA/% | 80.27 | 82.62 | 81.39 | 97.75 | 99.61 |
| AA/% | 68.32 | 76.51 | 75.22 | 97.54 | 99.65 | |
| Kappa×100 | 75.26 | 79.25 | 81.20 | 97.44 | 99.78 | |
| Salinas scene | OA/% | 96.34 | 85.00 | 94.20 | 98.06 | 99.96 |
| AA/% | 94.36 | 89.63 | 96.66 | 98.80 | 99.94 | |
| Kappa×100 | 95.93 | 83.20 | 93.61 | 97.85 | 99.95 | |
| Pavia University | OA/% | 96.63 | 96.34 | 95.95 | 98.40 | 99.97 |
| AA/% | 94.84 | 97.03 | 97.52 | 97.89 | 99.97 | |
| Kappa×100 | 95.53 | 94.90 | 93.40 | 97.89 | 99.96 |
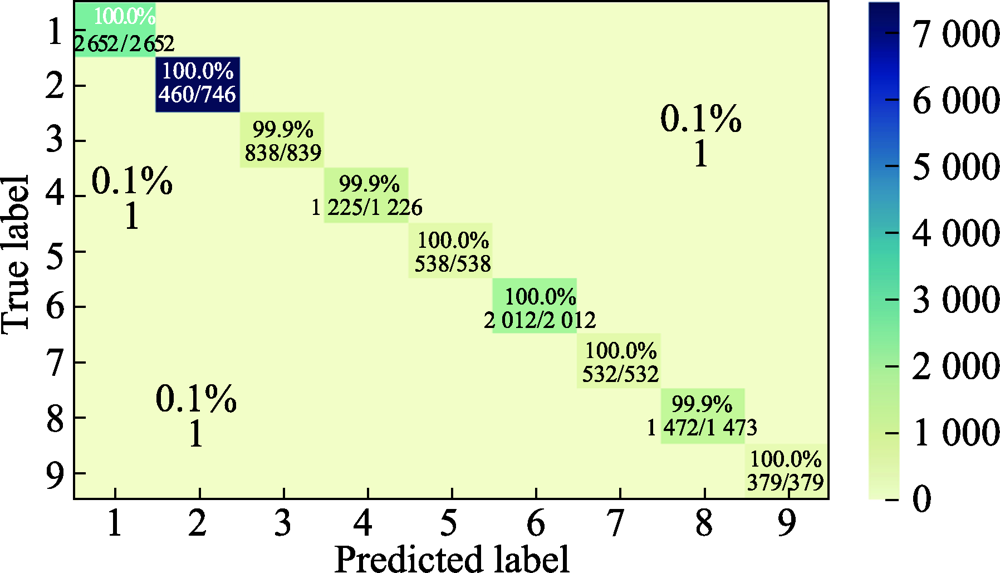
图12 在PU数据集上的混淆矩阵 类别1=Asphalt,类别2=Meadows,类别3=Gravel,类别4=Trees,类别5=Painted metal sheets,类别6=Bare Soil,类别7=Bitumen,类别8=Self-Blocking Bricks,类别9=Shadows
Fig.12 Confusion matrix on PU dataset
| [1] | 张兵. 高光谱图像处理与信息提取前沿[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5): 1062-1090. |
| ZHANG B. Hyperspectral image processing and information extraction[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(5): 1062-1090. | |
| [2] | 张淳民, 穆廷魁, 颜廷昱, 等. 高光谱遥感技术发展与展望[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2018, 39(3): 104-114. |
| ZHANG C M, MU Y K, YAN T Y, et al. Overview of hyper-spectral remote sensing technology[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2018, 39(3): 104-114. | |
| [3] |
ZHAO W Z, DU S H. Spectral-spatial feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification: a dimension reduction and deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4544-4554.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LIU Y F, LI X R, FENG Y M, et al. Representativeness and redundancy-based band selection for hyperspectral image clas-sification[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(9): 3534-3562.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
佘海龙, 解山娟, 邹静洁. 标准分数降维的3D-CNN高光谱遥感图像分类[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(4): 169-175.
DOI |
| SHE H L, XIE S J, ZOU J J. 3D-CNN with standard score dimensionality reduction for hyperspectral remote sensing images classification[J]. Computer Engineering and Appli-cations, 2021, 57(4): 169-175. | |
| [6] |
YU C Y, HAN R, SONG M P, et al. A simplified 2D-3D CNN architecture for hyperspectral image classification based on spatial-spectral fusion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2485-2501.
DOI URL |
| [7] | CHEN Y S, LIN Z H, ZHAO X, et al. Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data[J]. IEEE Journal of Sele-cted Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sen-sing, 2014, 7(6): 2094-2107. |
| [8] | CHEN Y S, ZHAO X, JIA X P. Spectral-spatial classifica-tion of hyperspectral data based on deep belief network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Obser-vations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(6): 2381-2392. |
| [9] |
HU W, HUANG Y Y, LI W, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2015. DOI: 10.1155/2015/258619.
DOI |
| [10] | CHEN Y S, JIANG H L, LI C Y, et al. Deep feature extrac-tion and classification of hyperspectral images based on con-volutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geo-science & Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6232-6251. |
| [11] | ZHONG Z L, LI J, LUO Z M, et al. Spectral-spatial resi-dual network for hyperspectral image classification: a 3-D deep learning framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geosci-ence and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 847-858. |
| [12] | SELLAMI A, FARAH M, FARAH I R, et al. Hyperspectral imagery classification based on semi-supervised 3-D deep neural network and adaptive band selection[J]. Expert Sys-tems with Application, 2019, 129: 246-259. |
| [13] | HAN X F, JIANG T, ZHAO Z F, et al. Research on remote sensing image target recognition based on deep convolution neural network[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recogni-tion and Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(5): 1-20. |
| [14] | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Tran-sactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. |
| [15] |
FANG L, LIU G, LI S, et al. Hyperspectral image classi-fication with squeeze multibias network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(3): 1291-1301.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MA S J, LIU W K, CAI W, et al. Lightweight deep residual CNN for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on depthwise separable convolutions[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 57023-57036.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 曹渝昆, 桂丽嫒. 基于深度可分离卷积的轻量级时间卷积网络设计[J]. 计算机工程, 2020, 46(9): 95-100. |
| CAO Y K, GUI L Y. Design of lightweight temporal convo-lutional network based on depthwise separable convolution[J]. Computer Engineering, 2020, 46(9): 95-100. | |
| [18] |
KHAN Z Y, NIU Z D. CNN with depthwise separable convolutions and combined kernels for rating prediction[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 170: 114528.
DOI URL |
| [19] | AHMAd M, KHAN A M, MAZZARA M, et al. A fast and compact 3-D CNN for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 1-5. |
| [20] | BEN HAMIDA A, BENOIT A, LAMBERT P, et al. 3-D deep learning approach for remote sensing image classifica-tion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sen-sing, 2018, 56(8): 4420-4434. |
| [21] | CHEN S T, JIN M, DING J. Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification based on dense residual three-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Multimedia Tools and Appli-cations, 2021, 80(2): 1859-1882. |
| [22] | HE M Y, LI B, CHEN H H. Multi-scale 3D deep convo-lutional neural network for hyperspectral image classifica-tion[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Confe-rence on Image Processing, Beijing, Sep 17-20, 2017. Pisca-taway: IEEE, 2017: 3904-3908. |
| [23] | ROY S K, KRISHNA G, DUBEY S R. HybridSN: explo-ring 3-D-2-D CNN feature hierarchy for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Let-ters, 2020, 17(2): 277-281. |
| [1] | 张璐, 芦天亮, 杜彦辉. 人脸视频深度伪造检测方法综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(1): 1-26. |
| [2] | 王仕宸, 黄凯, 陈志刚, 张文东. 深度学习的三维人体姿态估计综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(1): 74-87. |
| [3] | 梁佳利, 华保健, 吕雅帅, 苏振宇. 面向深度学习算子的循环不变式外提算法[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(1): 127-139. |
| [4] | 王剑哲, 吴秦. 坐标注意力特征金字塔的显著性目标检测算法[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(1): 154-165. |
| [5] | 张祥平, 刘建勋. 基于深度学习的代码表征及其应用综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(9): 2011-2029. |
| [6] | 李冬梅, 罗斯斯, 张小平, 许福. 命名实体识别方法研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(9): 1954-1968. |
| [7] | 任宁, 付岩, 吴艳霞, 梁鹏举, 韩希. 深度学习应用于目标检测中失衡问题研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(9): 1933-1953. |
| [8] | 杨才东, 李承阳, 李忠博, 谢永强, 孙方伟, 齐锦. 深度学习的图像超分辨率重建技术综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(9): 1990-2010. |
| [9] | 吕晓琦, 纪科, 陈贞翔, 孙润元, 马坤, 邬俊, 李浥东. 结合注意力与循环神经网络的专家推荐算法[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(9): 2068-2077. |
| [10] | 安凤平, 李晓薇, 曹翔. 权重初始化-滑动窗口CNN的医学图像分类[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(8): 1885-1897. |
| [11] | 曾凡智, 许露倩, 周燕, 周月霞, 廖俊玮. 面向智慧教育的知识追踪模型研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(8): 1742-1763. |
| [12] | 刘艺, 李蒙蒙, 郑奇斌, 秦伟, 任小广. 视频目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(7): 1504-1515. |
| [13] | 赵小明, 杨轶娇, 张石清. 面向深度学习的多模态情感识别研究进展[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(7): 1479-1503. |
| [14] | 夏鸿斌, 肖奕飞, 刘渊. 融合自注意力机制的长文本生成对抗网络模型[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(7): 1603-1610. |
| [15] | 孙方伟, 李承阳, 谢永强, 李忠博, 杨才东, 齐锦. 深度学习应用于遮挡目标检测算法综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(6): 1243-1259. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
